Hi together,
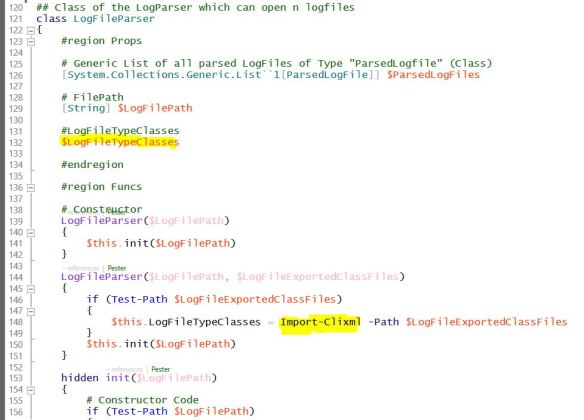
i created a LogFileParser (continuation from here), which can handle till now 4 different LogFileTypes:
SCCM-Logs
DISM
CBS
Upgrade-Logs
It´s written for Powershell v5, because it makes use of classes and i wanted to show you, how you can work with enums and classes.
Here is how you can make use of it: (can be found in Examples.ps1)

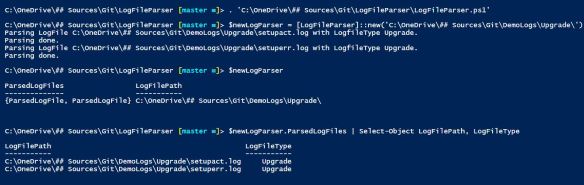


Download: https://github.com/ddneves/LogFileParser
Its code is written with Powershell classes which can be easily extended with additional helper functions or new LogFileTypes.
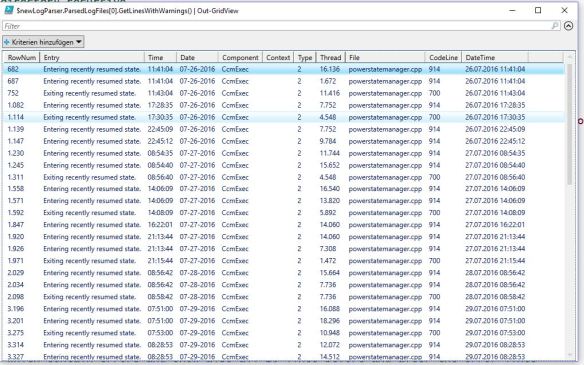
I integrated also a helper function to retrieve a range of cells before and after defined cell rownumbers. I used it to gather all rows, which contain “*error*” and all the 20(x) rows before and after for a whole file.
#requires -Version 5
<#
.NOTES
===========================================================================
Created on: 07.08.2016
Created by: David das Neves
Version: 0.1
Project: LogAnalyzer
Filename: LogFileParser.ps1
===========================================================================
.DESCRIPTION
Parses Logfiles into the class ParsedLogFile, which is integrated in the class LogFileParser
#>
## Enumeration of the LogFileTypes
enum LogFileTypes {
SCCM
CBS
Upgrade
DISM
}
## Class of the LogParser which can open n logfiles
class LogFileParser
{
#region Props
# Generic List of all parsed LogFiles of Type "ParsedLogfile" (Class)
[System.Collections.Generic.List``1[ParsedLogFile]] $ParsedLogFiles
# FilePath
[String] $LogFilePath
#endregion
#region Funcs
# Constructor
LogFileParser($LogFilePath)
{
# Constructor Code
if (Test-Path $LogFilePath)
{
$allLogFiles = Get-ChildItem $LogFilePath -Filter *.log -Recurse
$this.ParsedLogFiles = New-Object -TypeName System.Collections.Generic.List``1[ParsedLogFile]
$this.LogFilePath = $LogFilePath
foreach ($file in $allLogFiles)
{
$fileType = Get-LogFileType $file.Name
$this.ParsedLogFiles.Add([ParsedLogFile]::new($file.FullName, $fileType))
}
}
else
{
Write-Error -Message 'Path was not reachable. Please verify your Path.'
}
}
#endregion
}
class ParsedLogFile
{
#region Props
#Hidden variable for the keys in the logfile.
hidden [string[]] $ColumnNames
# FilePath of the parsed log.
[string] $LogFilePath
#The parsed logging data.
$ParsedLogData
#LogFileType for this file
[LogFileTypes] $LogFileType
#endregion
#region Funcs
## standard constructor
## LogFileType SCCM is set
ParsedLogFile($LogFilePath)
{
$this.LogFileType = [LogFileTypes]::SCCM
$this.LogFilePath = $LogFilePath
$this.LogFileType = $this.LogFileType
$this.Init()
}
## Constructr with LogFileType
ParsedLogFile($LogFilePath, $LogFileType)
{
$this.LogFilePath = $LogFilePath
$this.LogFileType = [LogFileTypes]$LogFileType
$this.Init()
}
## Initialization of class and log
hidden Init()
{
if (Test-Path -Path $this.LogFilePath)
{
# Constructor Code
$this.LogFilePath = $this.LogFilePath
Write-Host -Object "Parsing LogFile $($this.LogFilePath) with LogfileType $($this.LogFileType)."
$actualParsedLog = Get-RegExParsedLogfile -Path $this.LogFilePath -LogFileType $this.LogFileType
Write-Host -Object 'Parsing done.'
$this.ParsedLogData = $actualParsedLog.Log
$this.ColumnNames = $actualParsedLog.Keys
}
else
{
Write-Error -Message "Path was not reachable. Please verify your Path: $($this.LogFilePath)."
}
}
# Returns the column Keys
[string[]] GetColumnNames()
{
return $this.ColumnNames
}
# Returns lines with errors
[int[]] GetLinesWithErrors()
{
$LinesWithErrors = ($this.ParsedLogData).Where{
$_.Entry -like '*error*'
}
return $LinesWithErrors
}
# Returns lines with errors
[int[]] GetLinesWithErrorsHeuristic()
{
$LinesWithErrors = (($this.ParsedLogData).Where{
$_.Entry -like '*error*'
}).RowNum
$RowList = Get-RowNumbersInRange $LinesWithErrors
$ShowingRows = ($this.ParsedLogData).Where{
$_.RowNum -in $RowList
}
return $LinesWithErrors
}
# Returns lines with errors
# Overload with Range
[int[]] GetLinesWithErrorsHeuristic([int]$Range)
{
$LinesWithErrors = (($this.ParsedLogData).Where{
$_.Entry -like '*error*'
}).RowNum
$RowList = Get-RowNumbersInRange $LinesWithErrors -Range $Range
$ShowingRows = ($this.ParsedLogData).Where{
$_.RowNum -in $RowList
}
return $LinesWithErrors
}
# Returns lines with errors
[int[]] GetRowNumbersWithErrors()
{
$LinesWithErrors = (($this.ParsedLogData).Where{
$_.Entry -like '*error*'
}).RowNum
return $LinesWithErrors
}
#endregion
}
function Get-RowNumbersInRange
{
<#
.Synopsis
Get-RowNumbersInRange
.DESCRIPTION
Heuristic method, which returns a list of all transmitted rowlines addiing a number of lines n ($Range) before and after.
.EXAMPLE
$rowsWithErrors = 21,345,456
$allRowsToSHow = Get-RowNumbersInRange -RowNumbers $rowsWithErrors -Range 10
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param
(
#Previous calculated set of rowNumbers.
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName = $true,
Position = 0)]
$RowNumbers,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false,
Position = 1)]
[int]$Range = 20
)
Begin
{ }
Process
{
$allShowingRowNumbers = New-Object -TypeName System.Collections.Generic.List``1[Int]
foreach ($rowNum in $RowNumbers)
{
$min = $rowNum - $Range
$max = $rowNum + $Range
for ($x = $min; $x -lt $max; $x += 1)
{
$allShowingRowNumbers.Add($x)
}
}
$allShowingRowNumbers
}
End
{ }
}
function Get-LogFileType
{
<#
.Synopsis
Get-LogFileType
.DESCRIPTION
Returns the type of the transmitted LogFile.
.EXAMPLE
$LogFileType = Get-LogFileType -LogFileName 'dism.log'
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param
(
#Name of the logFile
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName = $true,
Position = 0)]
$LogFileName
)
Begin
{ }
Process
{
switch ($LogFileName)
{
#DISM
{
$_ -like 'dism*'
}
{
[LogFileTypes]::DISM
break
}
#Upgrade
{
$_ -like 'setupact*'
}
{
[LogFileTypes]::Upgrade
break
}
{
$_ -like 'setuperr*'
}
{
[LogFileTypes]::Upgrade
break
}
#CBS
{
$_ -like 'cbs*'
}
{
[LogFileTypes]::CBS
break
}
#SCCM
default
{
[LogFileTypes]::SCCM
}
}
}
End
{ }
}
function Get-RegExParsedLogfile
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Returns a ordered hashtable list for a log by using Regex.
.DESCRIPTION
The Regular Expression splits a single line of the log file into named keys.
This is used for a whole log file and a ordered hashtable list is returned.
.EXAMPLE
$parsedLogFile = Get-RegExParsedLogfile -Path 'c:\windows\CCM\ccmexec.log' -LogFileType SCCM | Out-GridView
.EXAMPLE
Get-RegExParsedLogfile -Path 'c:\windows\logs\cbs\cbs.log' -LogFileType CBS | Out-GridView
.EXAMPLE
cls
$parsedLogFile = Get-RegExParsedLogfile -Path 'c:\windows\logs\cbs\cbs.log'
$parsedLogFile.Log.Line | Where-Object { $_ -like '*error*' }
The Logfile is written into the hastable with the integrated key "Line".
You can filter these with where.
.EXAMPLE
$rx = '(?<Date>\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2})\s+(?<Time>(\d{2}:)+\d{2}),\s+(?<Type>\w+)\s+(?<Component>\w+)\s+(?<Message>.*)$'
$parsedLogFile = Get-RegExParsedLogfile -Path 'c:\windows\logs\cbs\cbs.log' -RegexString $rx
$parsedLogFile.Keys
.EXAMPLE
$rx='<!\[LOG\[(?<Entry>.*)]LOG]!><time="(?<Time>.*)\.\d{3}-\d{3}"\s+date="(?<Date>.*)"\s+component="(?<Component>.*)"\s+context="(?<Context>.*)"\s+type="(?<Type>.*)"\s+thread="(?<Thread>.*)"\s+file="(?<File>.*):(?<CodeLine>\d*)">'
$parsedLogFile = Get-RegExParsedLogfile -Path 'c:\windows\CCM\ccmexec.log' -RegexString $rx
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
param
(
#Contains the log file destination.
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, Position = 0)]
[System.String]
$Path = 'c:\windows\logs\cbs\cbs.log',
#Contains the RegEx with named keys
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false, Position = 1)]
[System.String]
$RegexString = '(?<Line>.*)$',
#ValidateSet of the differenct preconfigured LogFileTypes
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false, Position = 2)]
[LogFileTypes]$LogFileType = 'SCCM',
#Filter
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false, Position = 3)]
[System.String]
$GatherOnlyLinesWhichContain = ''
)
$t = (Get-Content -Path $Path -ReadCount 1000).Split([System.Environment]::NewLine)
if ($GatherOnlyLineWhichContain)
{
$t = $t| Select-String $GatherOnlyLinesWhichContain
}
[regex]$rx = $RegexString
# for each LogFileType a different Regex-String is used to parse the log.
switch ($LogFileType)
{
'SCCM'
{
$rx = '<!\[LOG\[(?<Entry>.*)]LOG]!><time="(?<Time>.*)\.\d{3}-\d{3}"\s+date="(?<Date>.*)"\s+component="(?<Component>.*)"\s+context="(?<Context>.*)"\s+type="(?<Type>.*)"\s+thread="(?<Thread>.*)"\s+file="(?<File>.*):(?<CodeLine>\d*)">'
break
}
'CBS'
{
$rx = '(?<Date>\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2})\s+(?<Time>(\d{2}:)+\d{2}),\s+(?<Type>\w+)\s+(?<Component>\w+)\s+(?<Message>.*)$'
break
}
'Upgrade'
{
$rx = '(?<Date>\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2})\s+(?<Time>(\d{2}:)+\d{2}),\s+(?<Type>\w+)\s{1,17}(\[(?<ErrorCode>\w*)\])?(?<Component>\s\w+)?\s+(?<Message>.*)'
break
}
'DISM'
{
$rx = '(?<Date>\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2})\s+(?<Time>(\d{2}:)+\d{2}),\s+(?<Type>\w+)\s{1,18}(?<Component>\w+)?\s+(?<Message>.*)'
break
}
default
{
Write-Error -Message 'Not Type has been set or found.'
}
}
[string[]]$names = 'RowNum'
$names += $rx.GetGroupNames() | Where-Object -FilterScript {
$_ -match '\w{2}'
}
[long]$rowNum = 0
$data = $t | ForEach-Object -Process {
$rx.Matches($_) | ForEach-Object -Process {
$match = $_
$names | ForEach-Object -Begin {
$hash = [Ordered]@{}
# $thisDate = $null
} -Process {
if ($_ -eq 'RowNum')
{
$rowNum += 1
$hash.Add($_, $rowNum)
}
elseif ($_ -eq 'Thread')
{
$hash.Add($_, [int]($match.groups["$_"].Value))
}
else
{
$hash.Add($_, $match.groups["$_"].Value)
}
} -End {
$thisDate=[datetime]($hash.Date + ' ' + $hash.Time)
$hash.Add('DateTime', $thisDate)
[PSCustomObject]$hash
}
}
}
$object = New-Object -TypeName PSObject
$object | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name Keys -Value $names
$object | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name Log -Value $data
$object
}
I hope, you like it.
Best regards,
David